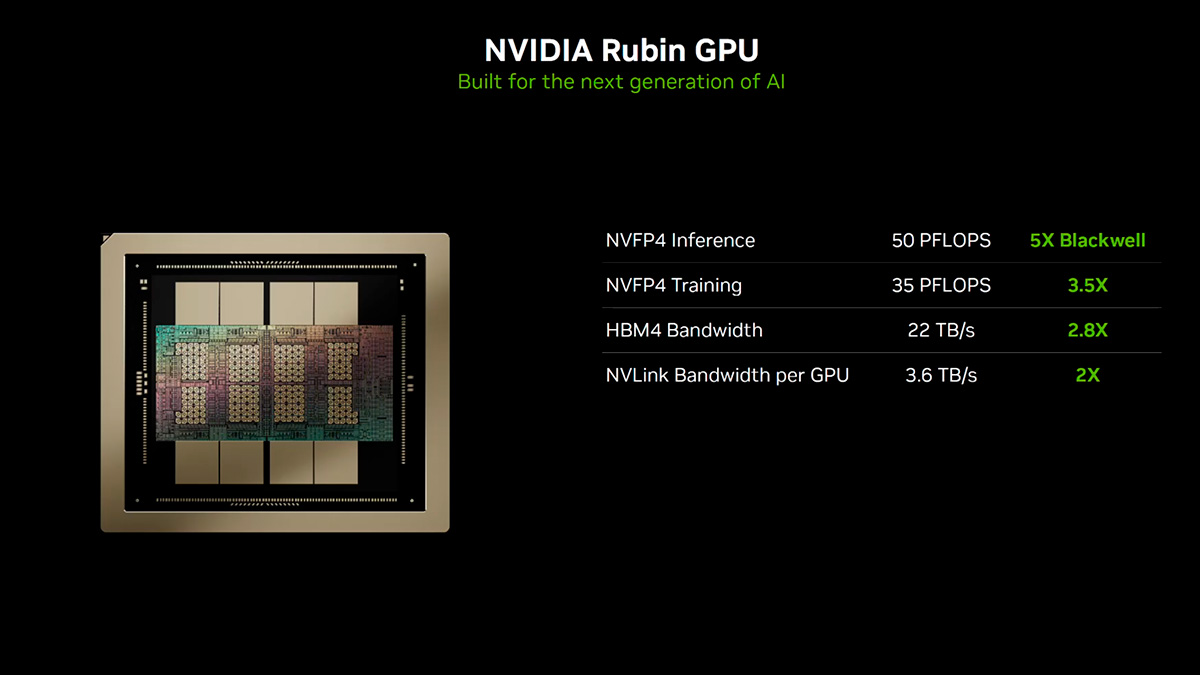
While the world is still getting used to the Blackwell architecture, NVIDIA has already unveiled its next giant leap in AI computing. The next-generation platform, named after astronomer Vera Rubin, is set to launch in the second half of 2026, promising to redefine the limits of artificial intelligence.
Technical Breakthroughs The Rubin architecture is designed to handle the massive workloads of future neural networks.
- Next-Gen HBM4 Memory: This is the game-changer. Moving to HBM4 allows for massive improvements in data transfer speeds and energy efficiency.
- Massive Capacity: Each GPU is expected to pack up to 288 GB of memory. This capacity is critical for running huge Large Language Models (LLMs) directly on the chip.
- "Vera" CPU: The new specialized CPU, named Vera, boasts a memory bandwidth of up to 1.5 TB/s, ensuring seamless communication between system components.
The Shift to Liquid Cooling With great power comes great heat. NVIDIA and key partners like Supermicro are preparing for a major infrastructure shift. Future systems based on Rubin (such as the NVL72 and NVL8 racks) will standardize Liquid Cooling. As chip density increases, traditional air cooling is no longer sufficient for top-tier data centers.
Why It Matters Despite high initial costs, the Rubin platform aims to lower the long-term cost of operation by significantly reducing the time required to train models like GPT-5 and GPT-6.
Conclusion from HYPERPC:
"At HYPERPC, we closely monitor these enterprise-grade innovations because they shape the future of desktop workstations. The move to HBM4 memory and mandatory liquid cooling in the Rubin architecture signals that the next generation of professional PCs will be more powerful—and more complex—than ever before. We are ready to bring this level of performance to our users."
Verified Sources:
- NVIDIA Blog: Inside the NVIDIA Rubin Platform
- Investing.com: Supermicro expands manufacturing for NVIDIA Vera Rubin
- Tom's Hardware / TechRadar Coverage
