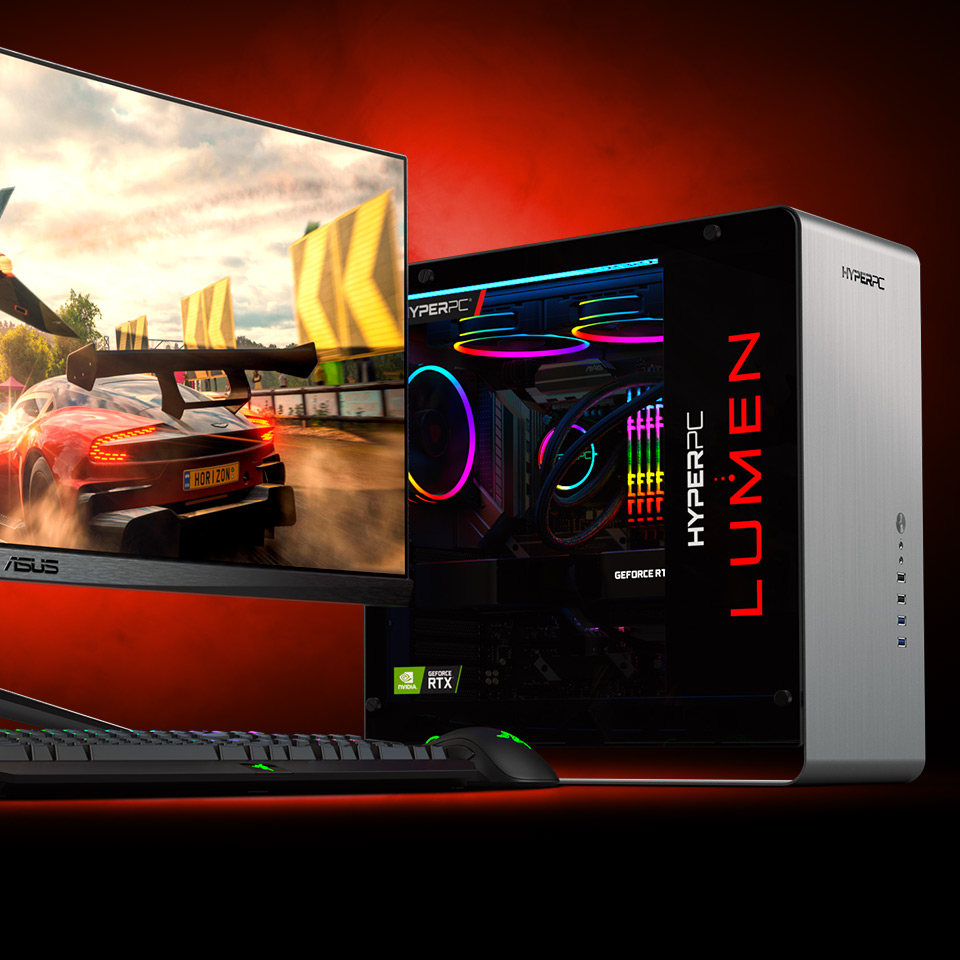
Gaming PCs with AMD Ryzen 5
The Ryzen 5 processors can be called the "golden mean" and the "optimal choice" for most gamers. With 6 cores, 12 threads, excellent single-core performance, super potential for overclocking, and a universal socket, these advantages are not possessed by their competitor, Intel.
Why is Ryzen 5 a gamer's CPU?
Anything weaker than this line will not allow you to crank up the graphics settings to the maximum in modern games. A gamer's build should be able to handle games in the way that developers intended. We need Ryzen 5 processors that are capable of handling FullHD, 2K, and 2.5K resolutions. They are weak for 4K, where video cards from another "weight category" are already used. They can also be used for VR, but not on top-of-the-line headsets.

High-core performance
Games mostly use up to 8 computational threads, but we have 12, and with excellent performance. This is if we are talking about relatively new projects, but many gamers prefer old games that have been running on the same engine for decades. Old platforms are not capable of working with more than one computational thread. For games like Lineage 2, World of Warcraft, or World of Tanks, high frequency on a single core is required.

Easy to upgrade
AMD releases all its processors under the same socket (the slot on the motherboard for the processor). You will be able to easily upgrade your PC in the future. If you have ever dealt with upgrading a computer on Intel, then you know that these guys like to create sockets for every new pebble. Such a policy is very inconvenient since it requires changing the motherboard, which increases the upgrade budget by $150-300.
TDP
A computer based on an AMD Ryzen 5 processor will be very quiet. The thermal design power (TDP) is only 65 watts for any model in the lineup. For example, the Intel Core i5-10600KF processor "eats" 125 watts. Almost all this energy is converted into heat and needs to be dissipated somewhere. Any cooling system is based on fans, even a liquid one simply delivers heat to a large radiator through prepared water, and the radiator itself is cooled by fans. The more heat needs to be dissipated, the more active the fans will work, creating noise.